Periodontitis (periodontosis) always treat consistently
Periodontitis, colloquially also called periodontosis, always needs to be treated. Otherwise, the jaw bone can recede in patients and the teeth can fall out.
- If left untreated, periodontitis and periodontosis can lead to tooth loss.
- Periodontal disease is closely linked to cardiovascular diseases.
- Chronic disease, which requires permanent aftercare.
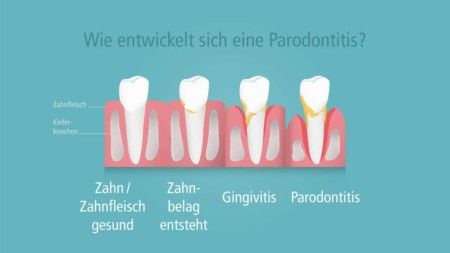
From bacteria to tartar to periodontitis, periodontal disease
Bacteria that adhere to the teeth are responsible for periodontitis, periodontosis. The bacteria join together to form a biofilm. If they are not removed by daily oral hygiene, they continue to grow and are visible to the naked eye as soft as well as hard plaque (tartar) on the teeth and in the spaces between the teeth. The body reacts to the bacteria with gum inflammation.
This is how he fights against them. Gums are red, swollen and can bleed easily. If the inflammation persists for a longer period of time, the bond between the gums and the tooth surface can tear and real gingival pockets develop. The deeper the gum pockets become in the course of the disease, the more bacteria they harbor and the more aggressive they are.
Bacteria can also get into the bloodstream and tissue. This can have far-reaching consequences. “Periodontitis is closely linked to cardiovascular and vascular diseases,” explains Dr. Michael Eremenko, Greifswald University Medical Center.
“In particular, the connection between periodontitis and an increased risk of heart attack has been known for a long time. If periodontitis is treated, diabetes patients can be better controlled. It reduces the late effects of diabetes.”Pregnant women also need to have periodontitis treated. Otherwise the risk of premature birth increases.
No plaque, no inflammation
Without plaque, inflammation cannot form in most people. The dentist or a specially trained employee therefore removes the hard and soft plaque in several sessions at the start of treatment. In general, if the teeth are thoroughly cleaned, polished and fluoridated, it is more difficult for bacteria to settle and the inflammation to recede.
The patient also receives intensive training in oral hygiene. The goal: improved tooth brushing at home and more intensive cleaning of interdental spaces. In most cases, these measures are sufficient to reduce inflammation.
Cleaning gum pockets
The dentist cleans deep gum pockets with many bacteria using ultrasound equipment and various hand instruments. If there is no change despite previous therapy, the dentist can clean the pockets again and also use an antibiotic. The dentist treats remaining deep pockets surgically. The dentist can clean better in areas that are difficult to access.
Aftercare is prevention
Periodontitis is a chronic disease. What does this mean for patients? Once you have periodontal disease, you have to follow up on a permanent basis. Depending on the risk of disease, the patient visits the dentist two to four times a year. Professional teeth cleaning (PZR) is part of the periodontal therapy. It contributes to the long-term success of the treatment. Experts also recommend regular PZR as a preventive measure.